Introduction #
BloodHound has been synonymous with red team work since its launch in 2016. BloodHound converts an analysis of an Active Directory or EntraID forest to a graph of lateral movement and privilege escalation opportunities.This graph view provides specific paths to reach a sensitive target, whether this is a Domain Admin account or a valuable data store. BloodHound is developed by SpecterOps and offers both commercial and open source options.
The BloodHound 8.0 release introduces OpenGraph; a model for importing graph data from nearly anything into the BloodHound tools. A library of extensions already includes everything from identity systems to SQL databases. If you can define a relationship between entities, you can shove it into BloodHound and analyze it with Cypher queries.
In a lot of ways, runZero’s Attack Graphs follow the BloodHound methodology; we use data about multi-homed systems, layer-2 topologies, layer-3 routing rules, and known vulnerabilities to demonstrate the “real” paths between systems in complex enterprise networks. With OpenGraph, we finally had an excuse to experiment with runZero data inside of the BloodHound graph.
We’re happy to share the result of one of these experiments; runZeroHound! This open source project parses an exported runZero Asset Inventory (JSONL format) and produces an import file for BloodHound. Since this is open source, feel free to tweak the graph generation logic, and add new nodes or edges as you see fit.
Schema #
At the time of release, this project supports the following schema:
Nodes
- RZAsset
- RZNetwork
- RZService
- RZDomain
- RZVLAN
Edges
- RZAssets are linked to RZNetwork using RZSubnetContains and RZInsideOfSubnet edges
- RZAssets are linked to RZService using RZHasService and RZRunOnAsset edges
- RZAssets are linked to RZDomain using RZDomainContains and RZPartOfDomain edges
- RZAssets are linked to RZVLAN using RZVLANContains and RZPartOfVLAN edges
- A “Global Internet” RZNetwork node is linked to other public RZNetwork CIDRs using RZSubnetContains and RZInsideOfSubnet edges
The RZAsset nodes include ALL columns, attributes, and foreign attributes. Cypher queries can account OS, Hardware, Risk, Vulnerability Count, and integrations like CrowdStrike Falcon or AWS.
The RZService nodes include ALL attributes, including fields like HTML Titles, SSH Banners, and Remote Desktop services.
Getting started with BloodHound Community Edition #
- Ensure that you have Docker or Podman (in Docker-compatbility mode). The command “docker compose ls” should not return an error
-
Git clone the BloodHound source tree:
git clone https://github.com/SpecterOps/BloodHound.git - Open a terminal in the BloodHound/examples/docker-compoose subdirectory
- Adjust docker-compose.yml to enable the “pg” graph-db driver:
bhe_graph_driver=pg - Adjust bloodhound.config.json to set the graph_driver to “pg”:
"graph_driver": "pg", - Run “docker compose up” to launch BloodHound
- Copy the initial admin password shown in the output
- Login to http://127.0.0.1:8080/ui/login with username admin and your password
- Change the password to something else and remember or save it
- Hurray! At this point you are ready to load and explore data
Getting started with runZeroHound #
- Ensure that you have a recent version of Go installed (1.25+)
-
Git clone the runZeroHound source tree:
git clone https://github.com/runZeroInc/runZeroHound.git - Ensure that the tool runs:
go run main.go -h
Download your runZero asset inventory in JSONL format #
- Login to your runZero Console
- Navigate to Inventory -> Assets
- Under Export, select “As JSON Lines…”
- Wait for this to download to disk
Create and import runZeroHound graphs #
- Open the runZeroHound directory in your terminal
- Run the convert command to create an OpenGraph JSON:
go run main.go convert <runZeroInventory.jsonl> opengraph.json - Use the Quick Upload option on the left and drag your opengraph.json onto it
- Watch the File Ingest history at http://127.0.0.1:8080/ui/administration/file-ingest
- Once import completes, access Explore and then select the Cypher tab
- Enter a test query to verify your data:
-
match (n:RZNetwork) where n.network_address = '0.0.0.0' return n - Confirm that this query shows the RZ-NETWORK-PUBLIC subnet node
The fun part #
With your OpenGraph data loaded, you can explore relationships between assets, services, networks, domains, and vlans.
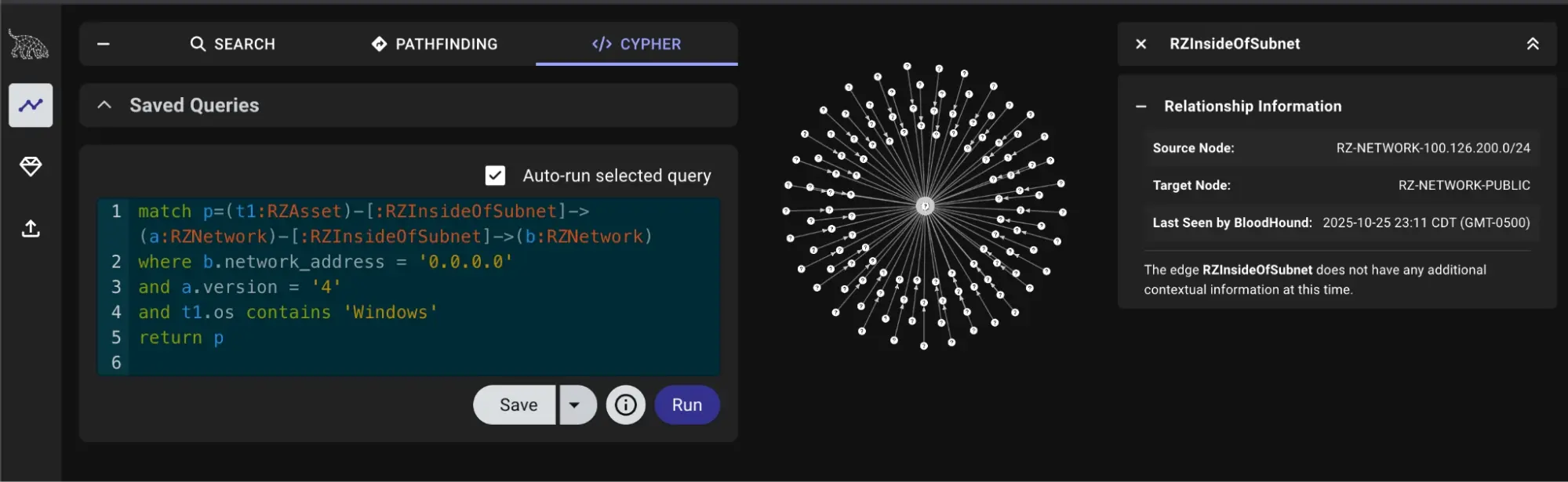
Windows machines with external IPs #
match p=(t1:RZAsset)-[:RZInsideOfSubnet]->(a:RZNetwork)-[:RZInsideOfSubnet]->(b:RZNetwork)
where b.network_address = '0.0.0.0'
and a.version = '4'
and t1.os contains 'Windows'
return p
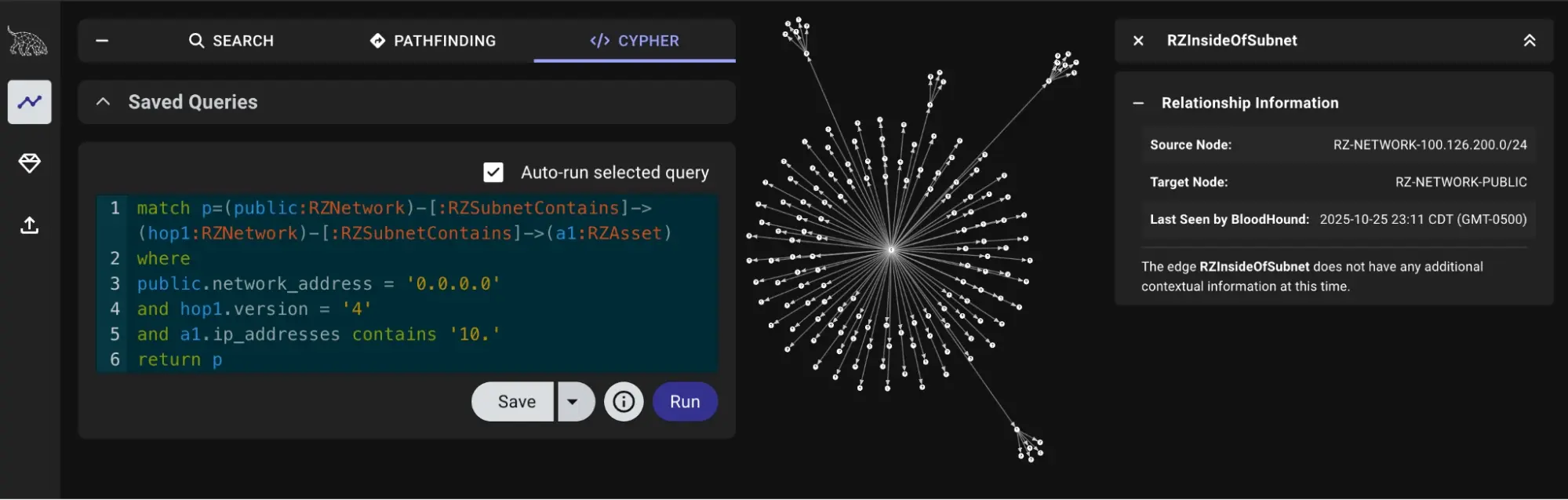
Paths from the internet to the internal 10.0.0.0/8 #
match p=(public:RZNetwork)-[:RZSubnetContains]->(hop1:RZNetwork)-[:RZSubnetContains]->(a1:RZAsset)
where
public.network_address = '0.0.0.0'
and hop1.version = '4'
and a1.ip_addresses contains '10.'
return p
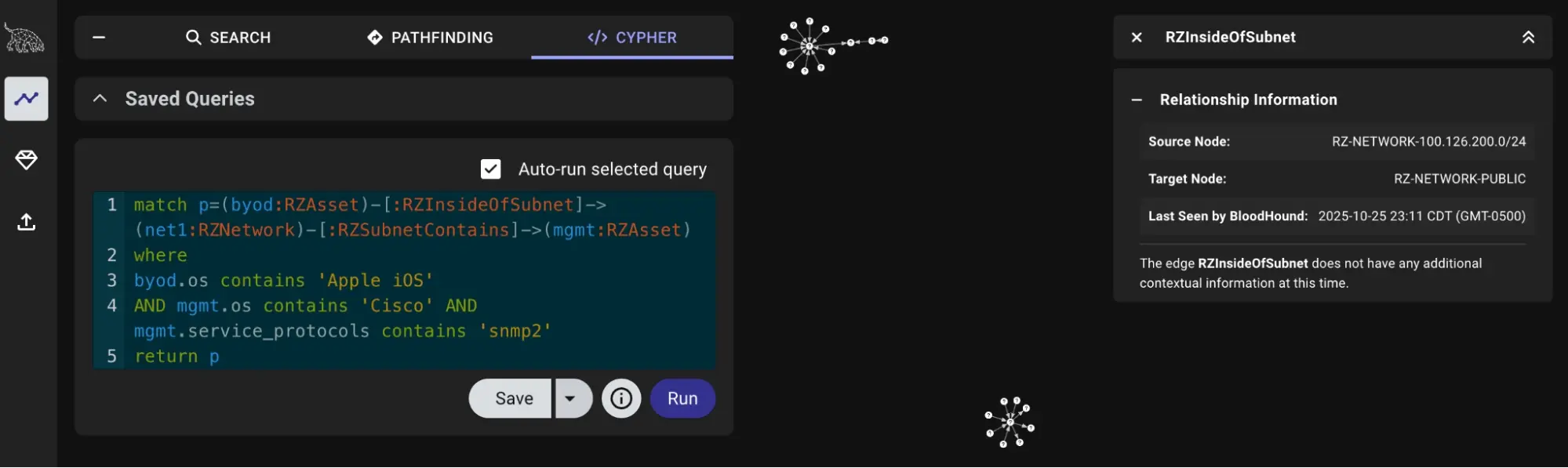
Find BYOD iPhones on same subnet as Cisco devices with default SNMP #
match p=(byod:RZAsset)-[:RZInsideOfSubnet]->(net1:RZNetwork)-[:RZSubnetContains]->(mgmt:RZAsset)
where
byod.os contains 'Apple iOS'
AND mgmt.os contains ‘Cisco’
AND mgmt.service_protocols contains 'snmp2'
return p
Summary #
We hope you enjoyed the dive into BloodHound OpenGraph and Cypher queries. To learn more we recommend checking out the OpenGraph overview and the Cypher documentation. Do you have any awesome idea for a Cypher query, or just a bug report or feedback? Please reach out to support@runzero.com and let us know!
If you haven’t used runZero before, time to fix that – start a trial account that can be converted to our free Community Edition at the end.
Watch the runZeroHound webcast #
Be sure to also check out this episode of runZero Hour with Tod Beardsley, Rob King and special guests HD Moore and Jared Atkinson, CTO of SpecterOps, as they dive into the tangled world of modern attack surfaces. See how runZero and Bloodhound combined forces to visualize complex attack paths, reveal hidden exposures, and help defenders think like adversaries.