Latest Citrix NetScaler vulnerability #
Citrix published Security Bulletin CTX694788 that documented a vulnerability that impacts customer-managed installations of NetScaler ADC (formerly Citrix ADC) and NetScaler Gateway (formerly Citrix Gateway) configured as a Gateway (VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy) or Authentication, Authorization and Auditing (AAA) virtual server are affected by a memory overflow vulnerability. This vulnerability has been designated CVE-2025-6543 and has been rated critical with a CVSS score of 9.2.
There is evidence that this vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
The following versions are affected
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 14.1 prior to 14.1-47.46
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.1 prior to 13.1-59.19
- NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS and NDcPP prior to 13.1-37.236-FIPS and NDcPP
What is the impact? #
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could allow an adversary to make unintended changes to control flow, potentially allowing remote code execution (RCE) or causing denial-of-service (DoS).
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Citrix recommends upgrading affected systems to one of the following versions as soon as possible:
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway to version 14.1-47.46 and later releases
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway to version 13.1-59.19 and later releases of 13.1
- NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS and 13.1-NDcPP to version 13.1-37.236 and later releases of 13.1-FIPS and 13.1-NDcPP
NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway versions 12.1 and 13.0 are end-of-life (EOL) and no longer supported. It is recommended to upgrade to one of the currently supported versions that address the vulnerabilities.
How do I find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero? #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
hw:="Citrix Netscaler Gateway" OR os:="Citrix ADC"June 2025: (CVE-2025-5777, CVE-2025-5349) #
Citrix published Security Bulletin CTX693420 that documented two vulnerabilities that impact customer-managed installations of NetScaler ADC (formerly Citrix ADC) and NetScaler Gateway (formerly Citrix Gateway). There is evidence that one of the vulnerabilities, designated by CVE-2025-5777, is being actively exploited in the wild.
- NetScaler configured as a Gateway (VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy) or Authentication, Authorization and Auditing (AAA) virtual server are at risk of an insufficient input validation vulnerability leading to memory out-of-bounds read in the NetScaler Management Interface which could allow access to secret values, bypass of protection mechanism, DoS or other unexpected results. This vulnerability has been designated CVE-2025-5777 and has been rated critical with a CVSS score of 9.3.
- An attacker with access to the NetScaler appliance IP (NSIP) address, Cluster Management IP (CLIP) address or local Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) Site IP (GSLBIP) address could utilize an improper access control vulnerability to gain access the the NetScaler Management Interface and its management functions. This vulnerability has been designated CVE-2025-5349 and has been rated high with a CVSS score of 8.7.
The following versions are affected
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 14.1 prior to 14.1-43.56
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.1 prior to 13.1-58.32
- NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS and NDcPP prior to 13.1-37.235-FIPS and NDcPP
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS prior to 12.1-55.328-FIPS
What is the impact? #
Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow an attacker to obtain sensitive information, potentially disrupt system operations and cause a denial-of-service, or gain control over the NetScaler Management Interface and its management functions potentially leading to system compromise.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Citrix recommends upgrading affected systems to one of the following versions as soon as possible:
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway to version 14.1-43.56 and later releases
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway to version 13.1-58.32 and later releases of 13.1
- NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS and 13.1-NDcPP to version 13.1-37.235 and later releases of 13.1-FIPS and 13.1-NDcPP
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS to version 12.1-55.328 and later releases of 12.1-FIPS
NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway versions 12.1 and 13.0 are end-of-life (EOL) and no longer supported. It is recommended to upgrade to one of the currently supported versions that address the vulnerabilities.
How do I find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero? #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
hw:="Citrix Netscaler Gateway" OR os:="Citrix ADC"February 2025: (CVE-2024-12284) #
Citrix issued a security bulletin for the on-premise NetScaler Console (formerly NetScaler ADM) and NetScaler Agent products. CVE-2024-12284 is rated high with a CVSS score of 8.8, which could lead to privilege escalation.
What is the impact? #
For customers running an on-premise installation of NetScaler Console with NetScaler Console Agents deployed, an authenticated remote attacker could "execute commands without additional authorization". NetScaler emphasized that an attacker must be authenticated, which limits the potential impact.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Citrix recommends upgrading to one of the following versions as soon as possible:
- NetScaler Console 14.1-38.53 and later releases
- NetScaler Console 13.1-56.18 and later releases of 13.1
- NetScaler Agent 14.1-38.53 and later releases
- NetScaler Agent 13.1-56.18 and later releases of 13.1
How do I find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero? #
From the Service Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
_asset.protocol:http AND protocol:http AND html.title:="NetScaler Console"June 2024: (CVE-2023-6548, CVE-2023-6549) #
In January Citrix published Security Bulletin CTX584986 that documented two vulnerabilities that impact NetScaler ADCs and Gateways. The most severe of these, CVE-2023-6549, was discovered and documented by BishopFox.
CVE-2023-6549 is rated high with a CVSS score of 8.2. This vulnerability is an unauthenticated out-of-bounds memory read which could be exploited to collect information from the appliance’s process memory, including HTTP request bodies. While serious, this is not thought to be a bad as the Citrix Bleed vulnerability due to the new vulnerability being less likely to leak high risk data.
CVE-2023-6548 is rated medium with a CVSS score of 5.5. This vulnerability is a code injection flaw that allows remote code injection by an authenticated attacker (with low privileged) with access to a management interface on one of the NSIP, CLIP or SNIP interfaces.
What is the impact? #
The vulnerability would enable an attacker to remotely obtain sensitive information from a NetScaler appliance configured as a Gateway or AAA virtual server via a very commonly connected Web interface, and without requiring authentication. CVE-2023-6549 is nearly identical to the Citrix Bleed vulnerability (CVE-2023-4966), except it is less likely to return highly sensitive information to an attacker. CVE-2023-6548 could be used by an attacker with credentials to execute code.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Citrix recommends limiting access to management interfaces as well as upgrading to one of the following versions:
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 14.1-12.35 and later releases
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.1-51.15 and later releases of 13.1
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.0-92.21 and later releases of 13.0
- NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS 13.1-37.176 and later releases of 13.1-FIPS
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS 12.1-55.302 and later releases of 12.1-FIPS
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-NDcPP 12.1-55.302 and later releases of 12.1-NDcPP
Warning: NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway version 12.1 is now End Of Life (EOL). Citrix advises customers to upgrade their appliances to one supported version that addresses the vulnerabilities.
How do I find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero? #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
product:netscaler OR product:"citrix adc"July 2023: (CVE-2023-3519) #
In July, 2023, Citrix alerted customers to three vulnerabilities in its NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway products. Surfaced by researchers at Resillion, these vulnerabilities included a critical flaw currently being exploited in the wild to give attackers unauthenticated remote code execution on vulnerable NetScaler targets (CVE-2023-3519). Compromised organizations included a critical infrastructure entity in the U.S., where attackers gained access the previous month and successfully exfiltrated Active Directory data. And at the time of publication, there appear to be over 5,000 public-facing vulnerable NetScaler targets.
What was the impact? #
The three reported vulnerabilities affecting NetScaler ADC and Gateway products were of various types, and each include different preconditions required for exploitation:
- Unauthenticated remote code execution (CVE-2023-3519; CVSS score 9.8 - "critical")
- Successful exploitation required the NetScaler target be configured as a Gateway (VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, or RDP Proxy) or "authentication, authorization, and auditing" (AAA) virtual server.
- Reflected cross-site scripting (XSS) (CVE-2023-3466; CVSS score 8.3 - "high")
- Successful exploitation required the victim to be on the same network as the vulnerable NetScaler target when the victim loaded a malicious link (planted by the attacker) in their web browser.
- Privilege escalation to root administrator (nsroot) (CVE-2023-3467; CVSS score 8.0 - "high")
- Successful exploitation required an attacker having achieved command-line access on a vulnerable NetScaler target.
U.S.-based CISA reported attackers exploiting CVE-2023-3519 to install webshells used in further network exploration and data exfiltration, causing CVE-2023-3519 to be added to CISA's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog. Other common attacker goals, like establishing persistence, lateral movement, and malware deployment, were all potential outcomes following successful exploitation.
Citrix made patched firmware updates available. Admins were advised to update older firmware on vulnerable NetScaler devices as soon as possible.
CISA also made additional information available around indicators of compromise and mitigations.
How to find potentially vulnerable NetScaler instances with runZero #
From the Asset inventory, they used the following prebuilt query to locate NetScaler instances on their network:
hw:netscaler or os:netscaler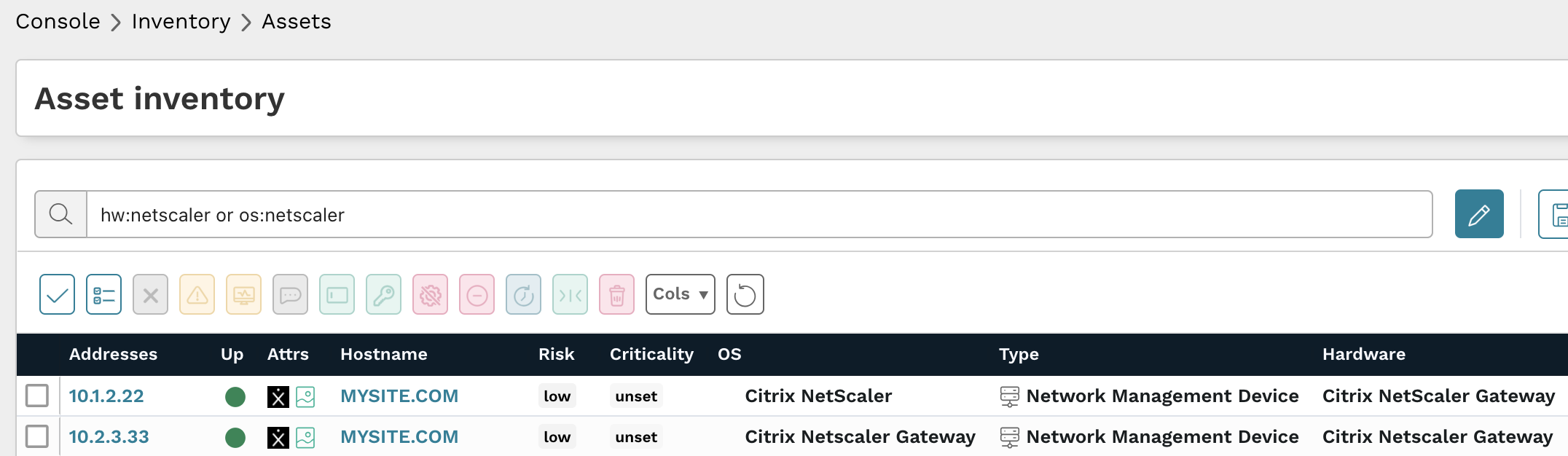
Results from the above query should be triaged to verify they are affected ADC or Gateway products and if they are running updated firmware versions.
The following query could also be used in on the Software and Services inventory pages to locate NetScaler software:
product:netscaler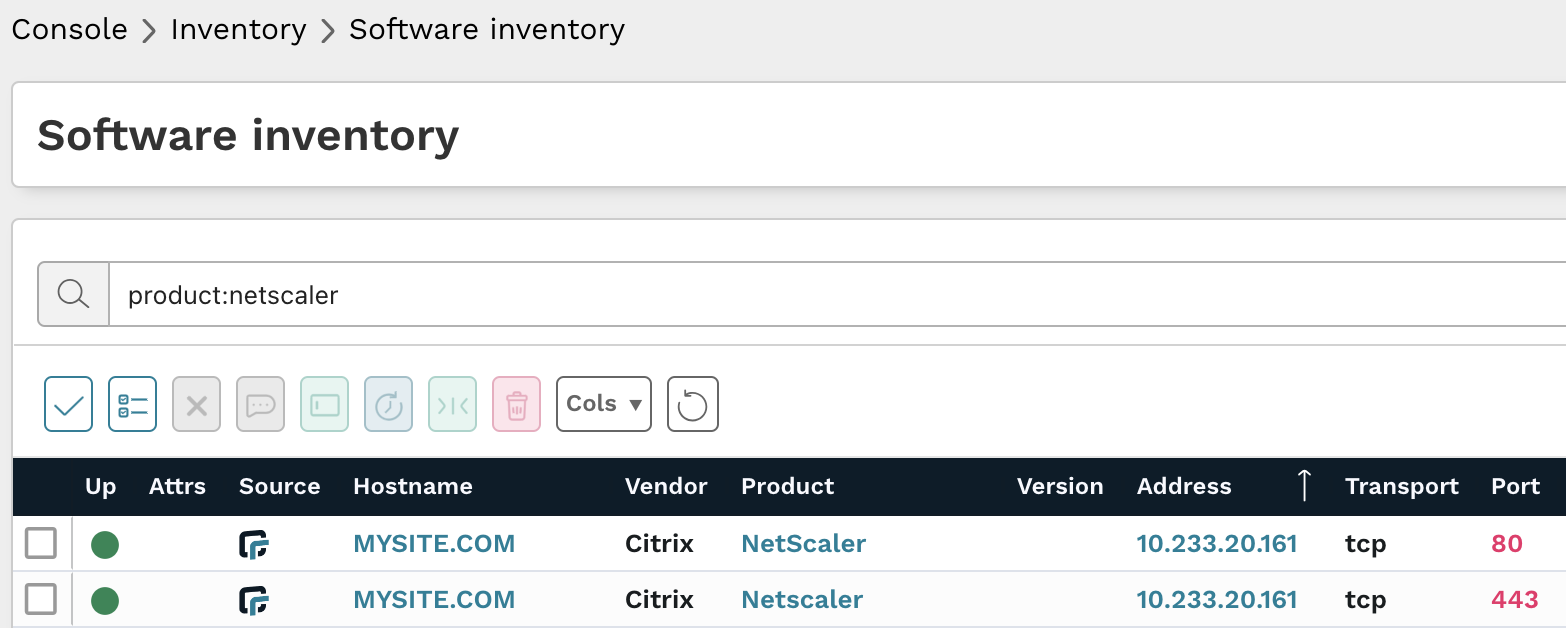
Results from the above query should be triaged to verify they are affected ADC or Gateway products and if they are updated versions.
As always, any prebuilt queries are available from your runZero console. Check out the documentation for other useful inventory queries.